AdminGuide:Service:SNMP
Return to AdminGuide:Service
Description
Protocol Operation
SNMP is the standard for network management and monitoring. Thus, it is a protocol used to monitor the state of a machine, specifically, to acquire from a monitoring server external to Kalliope status parameters related to CPU load, memory occupancy, disk space, and concurrent calls. It is a standard protocol available on Kalliope; OIDs (monitored objects) are made available on the central. Those defined in the standard MIB 2 are used, where object identifiers are made available through the agent. The server is the monitoring system that queries, while the SNMP agent is the service used to expose the data to a client that requests it. SNMP involves the client requesting the agent to find out the value of the OID, and the agent returns the value.
The data within the agent is organized in the form of a tree. The data indicate, for example, the version of the primary and secondary firmware, information regarding telephone services, the size of virtual memory occupied by the process, and the total number of failed authentication attempts by SIP clients.
Objects are defined as an index of a leaf under a parent: a tree structure allows you to access by specifying the path address between the subtrees to the leaf, which is the object you want to monitor. SNMP provides:
- Manager
- Agent
- Protocol
The representation of an OIP is done as a sequence of numbers, e.g., 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.6 is the path within the tree, and each point in the path has its textual correspondence.
Configuration
To enable NSMP support, go to "System Settings > SNMP Settings" and hit the "Enabled" checkmark.
The iReasoning MI Browser client was used for the configuration examples, it can make SNMP queries and shows the subtree organization.
System settings
[[File:Ireasoning.png|350px|destra]
The following information is mandatory; if it is not entered, the SNMP service cannot start.
- sysName: is a particular OID under the system tree (which is the first child and is denoted as 1.3.1.2.1.1), sysName is the machine name and is 1.3.6.1.2.1.5.0 (the 0 at the bottom since it is scalar type).
- sysLocation : is the physical location, it acts as a kind of inventory
- sysContact : email address of the contact person to contact if there is an anomaly in that particular node
In the defined settings, MIB tree 2 and host-resources (1.3.6.1.25) are the two that are exposed on Kalliope. Proprietary MIBs are also exposed and the software can read the whole tree since it scans it entirely, and it is the agent's job to return the values. The MIBs file allows the software monitoring to know the single leaf that only knows by number what it is.
SNMP access settings
- Listening address: e.g., by default 0.0.0.0 means it listens on all interfaces of the central unit. But, if we have a PBX with multiple network interfaces (some public and some private) and you want the SNMP service to be accessible from only one of these interfaces, you can put the IP address of the interface you want the service to be active. Then you can do a bind of the service on the IP entered; this must be one of the central unit's IPs (either one of its interfaces or that of the High Reliability in the case of a cluster). In the last case, in the case of HA, explicit monitoring should be done not pointing to the resource IP but the individual IPs of the two nodes.
- Listen port: 161 is the standard port since SNMP uses the UDP transport protocol.
- Community v1/v2: these are the basic versions of SNMP supported by monitoring systems, SNMP v3 support is not yet enabled. The default value that is used is "public"
- ACL': Access Control List, is a restriction on which IP address the client must have for querying. If an SNMP request comes in outside the ACL, it is rejected.
CAUTION: ACL 0.0.0.0/0 is not recommended, it is always good to restrict access only to authorized IPs
TRAP settings
Traps are a reactive-type mechanism that SNMP agents have for notifying the occurrence of events. Kalliope has not added specifications to the system, and basic ones are present:
- 0: ColdStart
- 1: WarmStart
- 2: linkDOwn
- 3: linkUp
- 4: authenticationFailure
- 5: egpNeighbortLoss
- 6: enterpreseSpecific
Directions on the configuration of TRAPs:
- TRAP send mode: specify whether you want to send the trap in version 1 or 2
- TRAP destination address: indicate IP address of the monitoring server to send TRAPs to
- TRAP destination port: e.g. 162 is the standard one
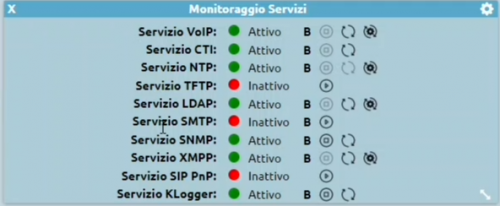
Sulla dashboard viene indicata l’esecuzione del servizio SNMP tramite il pallino verde e lo stato “Attivo”.
È possibile fare un’interrogazione dell’agent su Kalliope tramite un qualunque client SNMP (in questo caso si utilizza il già sopracitato iReasoning MIB Browser). Bisogna indicare l’indirizzo IP a cui collegarsi e poi impostare
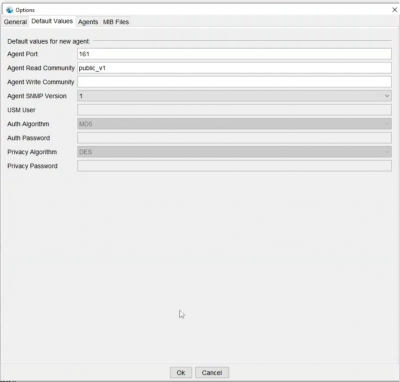
- Agent NSMP Version: i valori di default con cui fare la richiesta, ovvero si può scegliere se farla in versione 1 o 2
- Agent Read Community: qual è la community di lettura per poter avere accesso ai dati
- Agent Port: si può indicare la porta standard, 161
- Agent Write Community: non è abilitata la possibilità di fare scrittura tramite SNMP
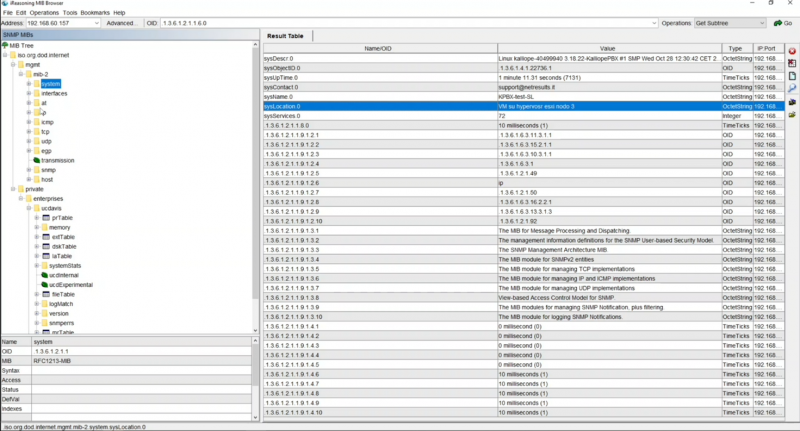
Dopo aver effettuato l'interrogazione è possibile leggere il contenuto dell’albero che è presente su Kalliope. La lettura può essere fatta oggetto per oggetto: Il sottoalbero system presente le seguenti informazioni tra cui il sysContact, il sysName e il sysLocation.
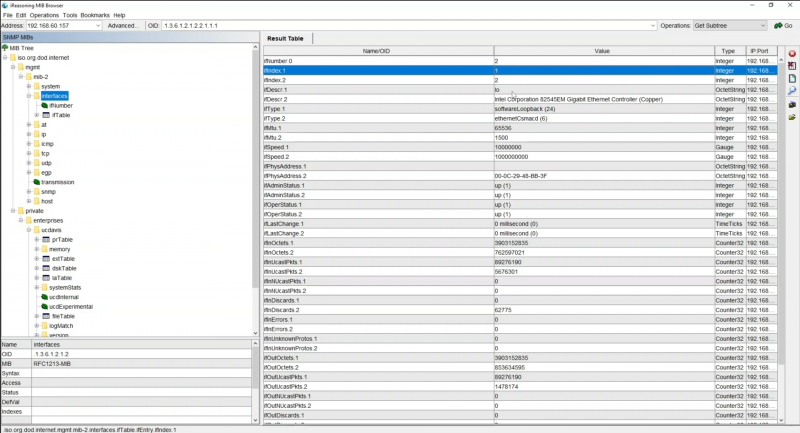
Il pannello interfaces restituisce le varie interfacce presenti e per ciascuna indica lo stato operativa e i byte scambiati in ingresso e uscita, questo permette ai sistemi di monitoraggio di far vedere il grafico dell’occupazione:
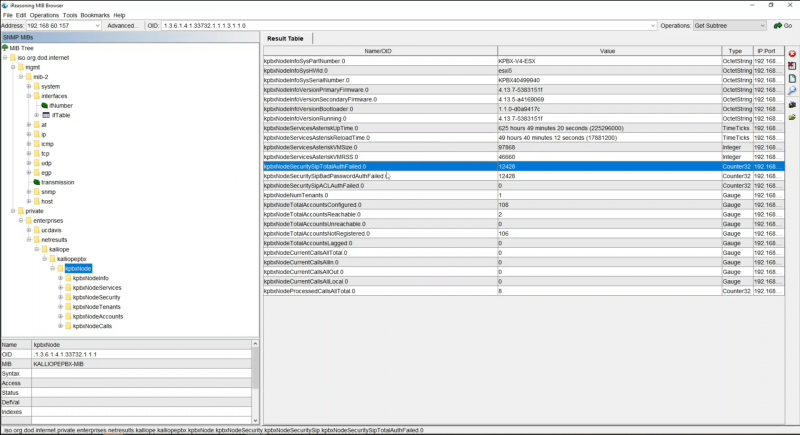
Esempio del kpbxNode:
N.B. Il contatore delle autenticazioni fallite (evidenziato in blu) è un dato importante poiché nel momento in cui dovesse arrivare un burst di autenticazioni fallite, probabilmente si tratterebbe di un attacco proveniente dall’esterno.
KalliopePBX espone delle MIB che consentono il monitoraggio del funzionamento dell’apparato tramite il protocollo di comunicazione standard SNMP.
Le MIB SNMP consultabili su Kalliope sono:
- MIB-II standard (RFC 1213) – Questa MIB definisce gli oggetti per la gestione e il monitoraggio di un apparato in una rete TCP/IP, in particolare su Kalliope sono implementati i seguenti sottoalberi: system, interfaces, at, ip, icmp, tcp, udp, transmission, snmp OID: 1.3.6.1.2.1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/10/11
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc1213/
- Host Resource MIB (RFC 2790) - Questa MIB definisce un insieme di oggetti contenenti la configurazione di host (server/computer) collegati ad una rete TCP/IP indipendentemente dal sistema operativo, dai servizi di rete e dalle applicazioni software installate. OID: 1.3.6.1.2.1.25
https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc2790/
- UCD-SNMP-MIB – Questa MIB definisce gli oggetti per il monitoraggio delle performance di un host (ad es. CPU /RAM / occupazione dischi). OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021
http://www.net-snmp.org/mibs/UCD-SNMP-MIB.txt
- Kalliope MIB: questa MIB proprietaria fornisce informazioni aggiuntive sulla configurazione e il funzionamento dei servizi implementati sul nodo Kalliope come ad es. numero di account configurati o registrati, chiamate contemporanee, numero totale di chiamate. OID:1.3.6.1.4.1.33732
Scarica i file di definizioni delle MIB: